In this article
Have you ever eaten a meal, and then a little while later find yourself salivating at the very thought of digging into a cheesy slice of pizza?
Your stomach might not be hungry, but your brain practically screams: “Eat!”
It all comes back to your hormone levels. And when you’re talking about weight loss, two major hormones can help or hinder your progress.
Chances are you’ve heard of ghrelin and leptin before. These are two hormones that play a big role in regulating appetite and controlling how much you eat.
Ghrelin, also known as the “hunger hormone,” is produced in the stomach and stimulates your appetite, signaling your brain when it’s time to eat.
Meanwhile, leptin tells your brain when it’s time to stop eating. It’s known as the “satiety hormone,” or sometimes the “starvation hormone.” Think of it as the knob that controls your body’s shutoff valve, telling it when it’s full.
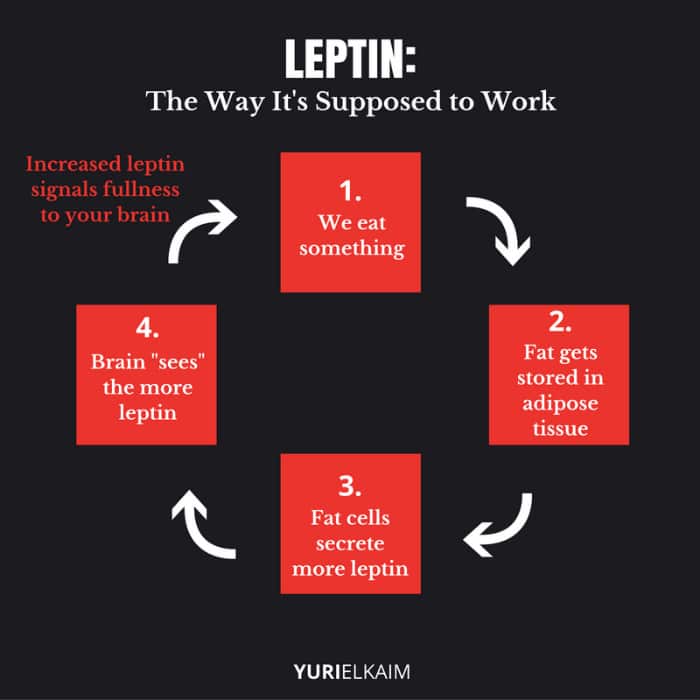
Ideally, your fat cells produce a set amount of leptin that help you maintain a state of energy balance – storing enough energy to keep your cells properly functioning while also keeping your weight stable (1).
As you might have guessed, changes in how much of these two hormones you have can change your appetite, how much you eat, and also your weight.
Ghrelin and Obesity
As you can imagine, the “hunger hormone” has ties to obesity. It’s often the culprit for those cravings that send you to the fridge for a not-so-healthy midnight snack.
And if you’ve ever found yourself elbow deep in a pint of ice cream after a stressful day at work, you can thank ghrelin for that too.
When you’re stressed – or feeling depressed or anxious – it can actually increase ghrelin levels in the brain, which leads to emotional and binge eating, even if you’re not hungry (2).
Some studies also suggest that ghrelin plays a role in your food reward system, acting on the brain’s “pleasure centers.” This is what can drive you to grab another slice of pizza – even though you’re not actually hungry – simply because you remember how good it felt eating the last one (3).
What causes uncontrolled ghrelin levels and an increased appetite?
For one, ever notice how you feel hungry when you’ve had a bad night of sleep? Lack of sleep can drive up ghrelin levels, making you feel hungry even when you’re not (4).
Insulin levels and ghrelin are also connected, which has an impact on people with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Some studies show that ghrelin affects insulin secretion as well as insulin receptors while others show that insulin levels have a direct effect on the amount of ghrelin circulating through your system (5).
Leptin and Weight Loss
Ghrelin isn’t the only hormone important in controlling your weight – leptin also plays a pivotal role, letting you know when you’re full.
When it works the way it’s supposed to, leptin is responsible for telling your brain that you’re done eating because you have enough food in your stomach and your cells have all the energy that they need.
Leptin is also important for regulating your energy balance long-term to control:
- how many calories you eat
- the amount of calories you use, and
- how much fat you are carrying on your body.
Basically it makes sure you don’t starve or overeat, but instead stay healthy and somewhere in the middle.
Because leptin is produced by your body’s fat cells, it makes sense that the more fat you’re carrying, the more leptin you produce.
When things are working the way they’re designed to, when you eat more, you have more fat on your body – and also more leptin. When the brain detects that there is more leptin, it signals you to stop eating.
But if you don’t have enough body fat, your leptin levels will drop, signaling the brain that it’s okay to eat more to bring leptin (and body fat) levels back up to a normal level.
Leptin Gone Awry
Anyway, that’s the way it’s supposed to work … but it doesn’t always happen like that.
When you’re obese, that means you have more fat cells – and also more leptin circulating in your body. Ideally, all that leptin floating around should signal the brain that there’s plenty of energy stored up so there’s no need to eat more.
But many obese people suffer from leptin resistance, which means the brain doesn’t detect all the leptin that’s there and instead tells the body to eat more and conserve energy by moving less (6).
As you can imagine, this can lead to weight gain in the long-term.
The main causes of leptin resistance include (7):
- Chronic inflammation: increased inflammatory markers in the blood can stop the transmission of leptin signals in the brain
- Increased levels of leptin: the development of leptin resistance is more likely with chronically elevated levels of leptin
Both inflammation and high levels of leptin are commonly seen in obesity, making the link between leptin resistance and weight control even stronger.
Symptoms of Leptin Resistance
Think you might be leptin resistant? Identifying the problem is the first step to improving your health.
Here are the three most common symptoms you should expect if you’re leptin resistant:
1. You Crave Foods
If you’re constantly snacking and never seem to feel satisfied, there’s a good chance you could be leptin resistant. When leptin isn’t able to signal to our brain that we’ve had enough to eat, it can cause endless hunger and cravings.
2. You’re Always Stressed and Tired
Both sleep deprivation and chronic stress can spike your levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that leads to leptin resistance, plus obesity, inflammation, and lots of other health problems (8).
3. You’re Overweight or Underweight
One of the biggest indicators that leptin isn’t quite working the way it’s supposed to is found right on your scale. Carrying extra weight (or not enough weight) is a pretty good sign that you could be leptin resistant (9).
How to Reverse Leptin Resistance
Though leptin resistance sounds pretty scary, there are steps you can take to prevent or reverse it.
In the end, it all comes back to reducing inflammation by changing the foods you’re including in your diet and modifying your lifestyle. Here are a few simple steps you can take to get on track to reversing leptin resistance:
1. Exercise
Incorporating more movement into your day is not only good for your waistline, but it can also improve leptin resistance. Increasing physical activity has been shown to decrease leptin concentrations, plus body mass index and fat mass (10).
Helpful Resources:
- How to Do Interval Training (The Right Way)
- Walking for Weight Loss: 2 Ways to Walk off 25 Pounds
- The 10-Minute Bodyweight Workout Routine Beginners Should Be Doing
2. Get More Sleep
Not getting enough sleep is one of the big risk factors for developing leptin resistance, and one of the best ways to fight it is by making sure you’re getting a solid eight hours each night. Studies show that leptin levels are influenced by how long you’re sleeping each night (11).
Helpful Resources:
- 10 Ways to Sleep Better Tonight (No Sleeping Pills Required)
- Circadian Rhythm and Sleep: 2 Tips for Sleeping Better
3. Follow an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Refined sugars, processed foods, and dairy are all commonly linked to inflammation and eating too much can lead to leptin resistance.
Instead, fill your diet with fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and healthy protein sources to minimize inflammation and prevent leptin resistance.
Helpful Resources:
4. Minimize Stress
Stress is another big contributor to leptin resistance, plus lots of chronic diseases, so it’s a good idea to find ways to cut back on your stress levels wherever possible. Instead of letting stress build up, look for ways to healthy reduce your anxiety and manage your stress.
Helpful Resource:
5. Eat More Fiber
Fiber is important when it comes to satiety and weight control. It moves slowly through your digestive system and keeps you feeling full and satisfied.
Not only can this help you lose weight, which aids in treating leptin resistance, but it can also help promote a healthy digestive tract and keep you regular.
Helpful Resources:
6. Avoid Grazing
All too often, many of us find ourselves snacking a little at a time, throughout the day. A bite or two here plus a snack or two there might not seem like much, but it can add up.
Instead of snacking all day long, establish a routine with a few meals each day and some healthy snacks in the mix. This can help keep leptin levels stable and prevent spikes that may come when you constantly eat during the day, making it much easier for the body to respond to leptin as it’s supposed to.
7. Increase Your Protein Intake
Eating enough protein not only helps with weight loss, but it can also prevent leptin resistance. Research shows that a high-protein diet reduces appetite, causes weight loss, and even decreases leptin levels.
I recommend sticking to high-quality and organic sources of protein whenever possible to promote overall health (12).
Helpful Resources:
- 21 Healthy High Protein Breakfasts You Need to Make
- 21 Vegan Slow Cooker Recipes That Will Never Fail You
Take Control of Your Hunger Hormones
If you’re having trouble losing weight, it could be a sign that there are more factors at play than just diet and exercise. The relationship between ghrelin, leptin and weight loss is clear and it could have a role in your weight troubles.
Instead of getting frustrated and repeating cycles of yo-yo dieting, treat your problem at the root by taking control of your hunger hormones.
Getting your leptin and ghrelin in balance and preventing and reversing leptin resistance can make a world of difference in keeping your appetite – and your weight – under control.
Burn Fat Even When You’re Asleep
Learn the keys to turning your body into a fat-burning machine, all day (and night!) long. Reset your metabolism by learning the 5-day food cycling formula that harnesses the power of your hormones.
Get your copy of the All-Day Fat Burning Diet and learn how to lose weight while still enjoying your favorite foods!
Click the banner below for all the details.